Europe enters 2026 with a firmer but still uneven economic foundation. Despite persistent pressures—from rising housing costs to fiscal divergence and external demand constraints—the region is showing signs of stabilization. Consumption is holding steady, inflation has largely converged, and employment remains near historic highs, providing businesses with a more predictable planning environment.
The latest Economic Outlook explores how government spending, stable energy prices, and reduced policy uncertainty following the US–EU deal supports a modest but resilient growth trajectory. It also examines the structural challenges that continue to shape the medium-term outlook, including supply-driven housing constraints, slower labor-force expansion, and delays in public-investment execution.
This month’s analysis provides a data-rich view into the trends defining Europe’s economic transition.
Key topics include:
- GDP outlook at ~2% SAAR for 2026
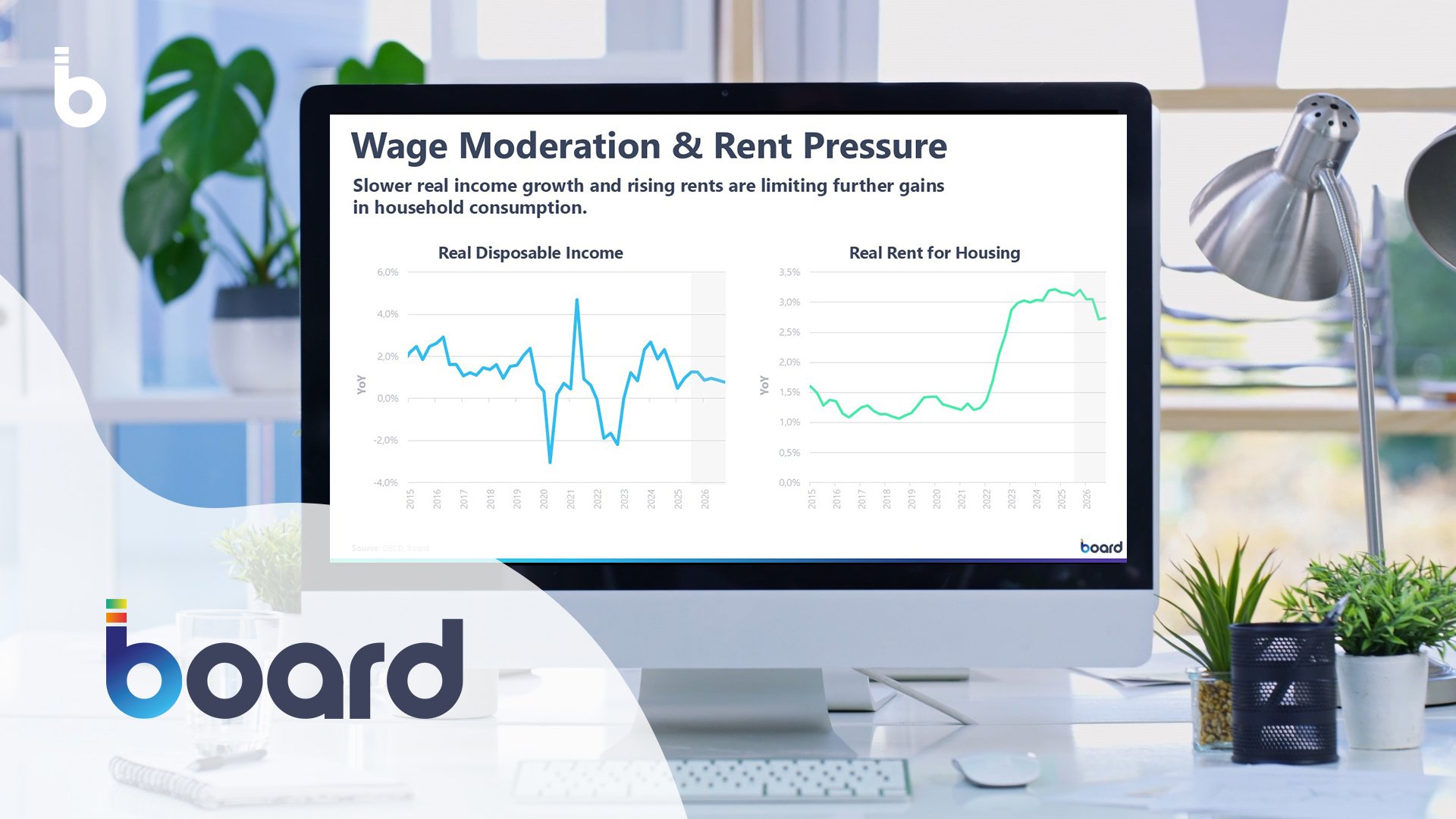
- Housing pressures, with prices rising ~3.6% YoY and rents ~3%
- Labor-market moderation and unemployment near 6%
- ECB policy stability as inflation converges
- Industrial production supported by fiscal stimulus but vulnerable to execution delays
Explore the full Europe Outlook to understand the forces shaping business planning for 2026 and beyond.